Laboratory and Cleanroom Accessories
Cabinets & Carts: ALLpaQ Innovation for your Cleanroom
Introducing the 2D Transfer Cabinet Picture this: You need a storage solution for a specific spot in your cleanroom, but […]
Apr 22nd, 2024
Cabinets & Carts: ALLpaQ Innovation for your Cleanroom
Apr 22nd, 2024
So, you’re at a party or other social gathering, and someone innocently asks: “So, what do you do?”
How do you distil the fermentation process that extracts living cells from microorganisms like bacteria and turns them into vaccines and other pharmaceuticals? How do you boil that down to its essence, so even a partygoer with a head full of champagne bubbles can understand it?
Bioprocess Fermentation has two parts: We’ve written at greater length about both Upstream bioprocessing in this blog, and Downstream bioprocessing in this one.
When that person in the party asks “What’s the difference ?” you can whip out this blog and leave them satisfied, informed and hopefully entertained, while you nip off and help yourself to some finger food, we’ve got this. We’re ALLpaQ and we’re happy to help!
The entire biopprocess follows this path:
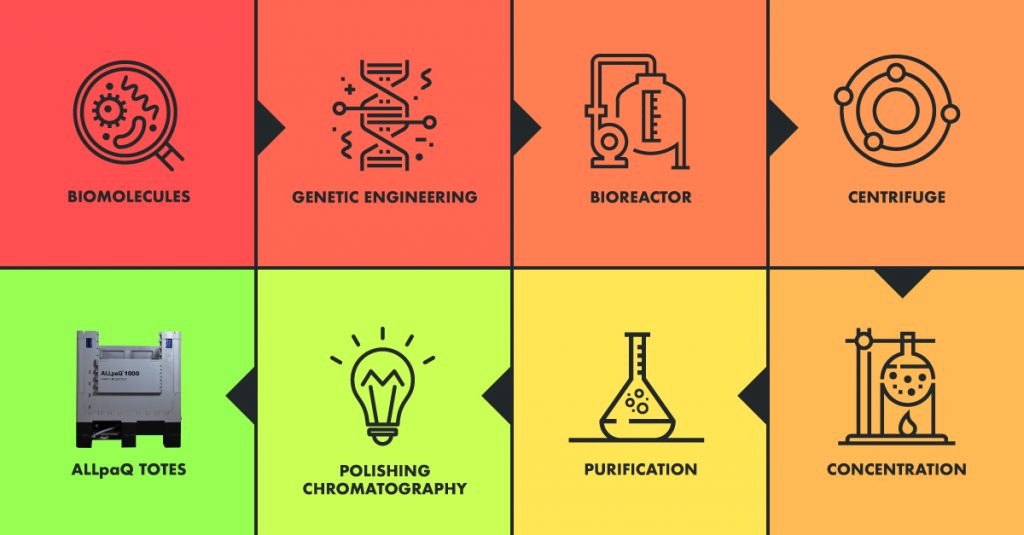
Now, let’s guide you through this little chart while you chew on that vol-au-vent (oh, and keep an eye our for the asparagus wrapped in prosciutto – they’re to die for!)
Upstream Processing (aka Cell Culture Processing) is the first half the journey. It includes the following steps, any of which are greatly aided by employing ALLpaQ’s range of 2D Bioprocess Accessories:
1: Biomolecules: The process begins with a source of therapeutic proteins – such as antibodies or enzymes.
2: Genetic Engineering: These proteins are introduced into cells using genetics or molecular biology. These cells then naturally produce more proteins.
3: Bioreactor: These protein factory cells are then encouraged to grow in a Bioreactor. This cell expansion vastly increases the amount of protein that is produced. When they reach the desired quantity (measured in litres) they are harvested.
At this stage they can be stored in ALLpaQ Cleanroom Totes and moved on to the next step: Downstream.
Downstream processing is all about purifying the ‘cell mass’ product, reducing any contaminants – to meet purity and quality standards – through processes such as centrifugation and filtration.
4: Centrifuge: Separation is the process where the desired molecules are separated from the mass of cell factories – by spinning the mix in a centrifuge.
5: Concentration: The concentration of active material coming out of the bioreactor can be quite low, so this process increases the proportion of active molecular matter in the mass. This can include vacuum drying to reduce the amount of water.
6: Purification: Several methods of purification can be employed, depending on the physico-chemical nature of the molecules being produced. Traditional methods such as fractional distillation can still be employed, which divided the mass into smaller, purer quantities.
7: Polishing: The final stage in making the product as pure as possible is ‘Column Chromatography’ which divides the remaining materials by the way they move through the column at different rates – a process which works at quantities from micrograms up to kilograms.
And the end of that process, the end product is typically between 98 – 100% pure, and that can be stored. This is typically done in vials or in 2D and 3D bags, which is where ALLpaQ Genesis Totes comes in, ready for shipping.
So, here at ALLpaQ, we’re equipped to support you throughout downstream and upstream bioprocessing, and we’ve even got you covered in social interactions.
*SAFETY NOTE: Please don’t let dummies anywhere near your Bioprocess equipment. Seriously. Unless you want a zombie apocalypse.
To talk more about your bioprocess needs, now and in the future:
Call +44 (0) 1472 800 373,
Email email enquiries@allpaq.com